Join
"The Marketing Mixtape"
Get the latest digital marketing insights straight to your inbox.
Send the right message, at the right time and to the right recipient.

Email marketing automation consists of sending the right message, at the right time and to the right recipient. Email marketing can be on the one hand, bulk emails sent to a specific list of recipients, and on the other hand, the creation of automation workflows. These workflows use predefined rules to trigger emails and personalise messages according to the specific actions that contacts do or do not perform.
Email marketing can be effective for any business that wants to reach a large number of people quickly and cheaply. These can be small businesses, large corporations, non-profit organisations or any other entity. It is especially useful for businesses that have a large list of leads or customers, or for those who want to build relationships with their customers and keep them informed of new products or services.
It is also a very important tool for those who wish to target specific groups, such as those who have expressed an interest in a particular product or service. This is because you can personalise marketing messages in an automated way and adapt them to the needs and interests of each recipient.
The advantage of email marketing is that it is very affordable. Regardless of the budget you wish to allocate, there is a solution for every type of need. As an example, here are three popular solutions on the market:
Each of these platforms offer different plans depending on the features you want to use. In addition to sending newsletters and creating workflow scenarios, they also allow you to create landing pages, forms, reports and even website hosting.
A trigger is a key element in the creation of automation scenarios. It corresponds to an action or an event carried out by a lead or a customer. For example, you can create a “Visit product page X” trigger and when your customers land on this page, a specific information appears in your database.
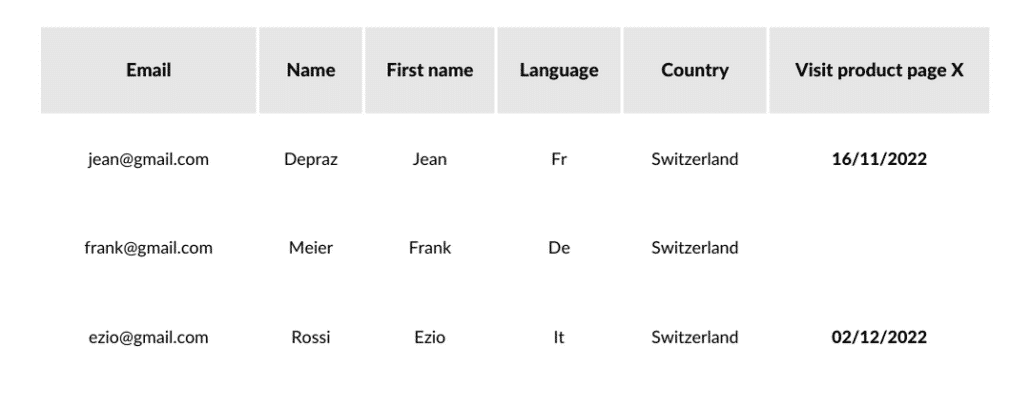
In this example, two of the three contacts visited the product X page. Furthermore, the desired response is a date, but any information could have been included. It could simply be “yes” if the contact visited the page or “no” if they did not.
Nevertheless, the most recent date of visit provides a more relevant data point:
This brings us to the importance of defining the right trigger, but also of choosing the right answer and its format. Generally, the response options are the following:
To conclude this example, we could define two additional triggers such as :
Together, these three triggers can be used to send a newsletter only to those contacts who have visited the product X page in the last 30 days, at least 3 times, and who have viewed the page for more than 2 minutes in cumulative time.
In order to convince them, there is nothing to stop you from offering them a discount coupon to make several additional sales.
The automation workflow (or scenario) refers to a set of conditions and actions through which one or more contacts flow. It is commonly represented in the form of an inverted tree, with the entry point(s) at the top and the last action(s) at the bottom.
Here is an example of a relatively basic workflow, the idea is not to propose something functional, but simply to explain how it works:
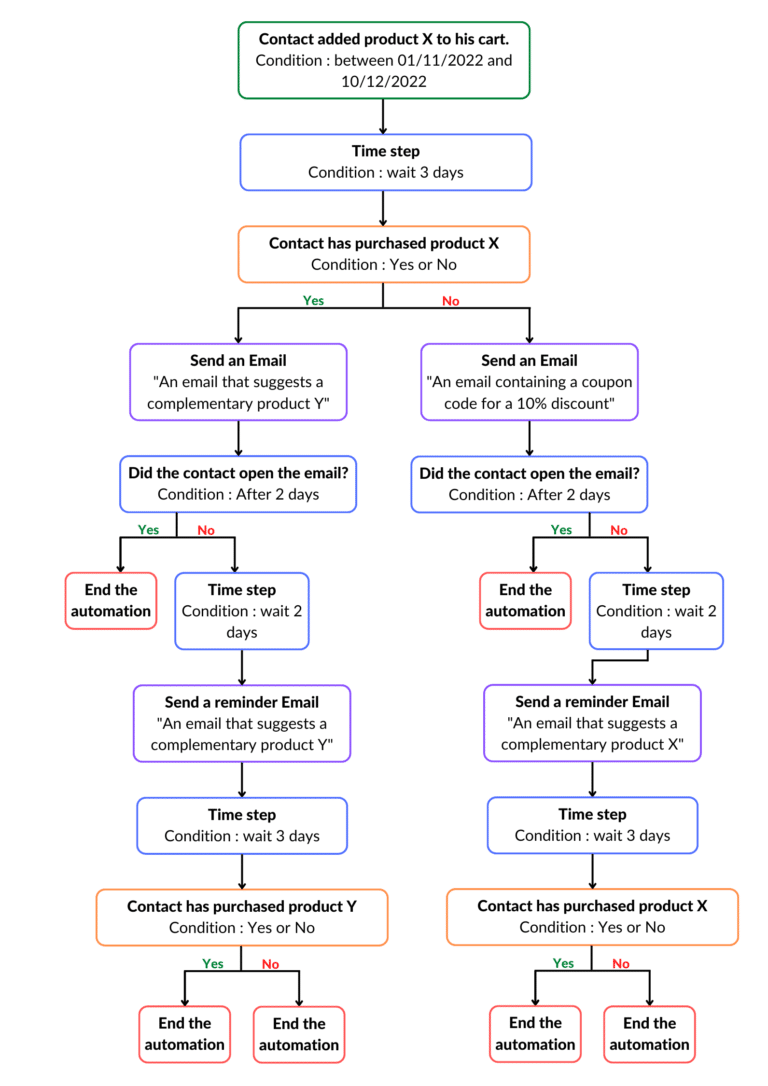
Assuming you want to make more sales for the holiday season, you activate this workflow on 31 October and deactivate it on 11 December.
Important point: these emails are purely marketing and not transactional! A transactional email is, for example, a purchase confirmation email. This type of email is never included in a marketing workflow.
In each workflow, conditions are used to specify when an email should be sent and to whom. This allows you to create a personalised and targeted email campaign, tailored to the needs and interests of each recipient.
Here are the different types of conditions that can be used:
By using a combination of different conditions, you can create highly personalised workflows, tailored to the needs and interests of your leads or customers.
Do not ignore the General Data Protection Regulation!
GDPR requires companies to obtain explicit consent from individuals before sending them emails. This means that companies must obtain their permission and must provide clear information about how personal data will be used. The regulation also gives individuals the right to opt out of receiving marketing emails at any time, and requires companies to provide an easy way to do so.
Overall, businesses need to ensure that they are compliant with this regulation in order to avoid fines and other penalties.
To adhere to GDPR requirements,, it is very important to let the contact choose to receive this type of marketing email. This is called Opt-In or double Opt-In when the verification is done in two steps (the contact must have clicked on a link in a registration confirmation email before they can receive any further emails from a company or organisation).
Even if the number of people is naturally reduced since their agreement is necessary, email marketing remains one of the most effective and easy to implement sales or loyalty techniques.
Contact us today to find out how we can help your business grow with effective automation workflows!
Get the latest digital marketing insights straight to your inbox.
